Accounting for risks and uncertainties in forest-based businesses, sectoral projections, and policy design
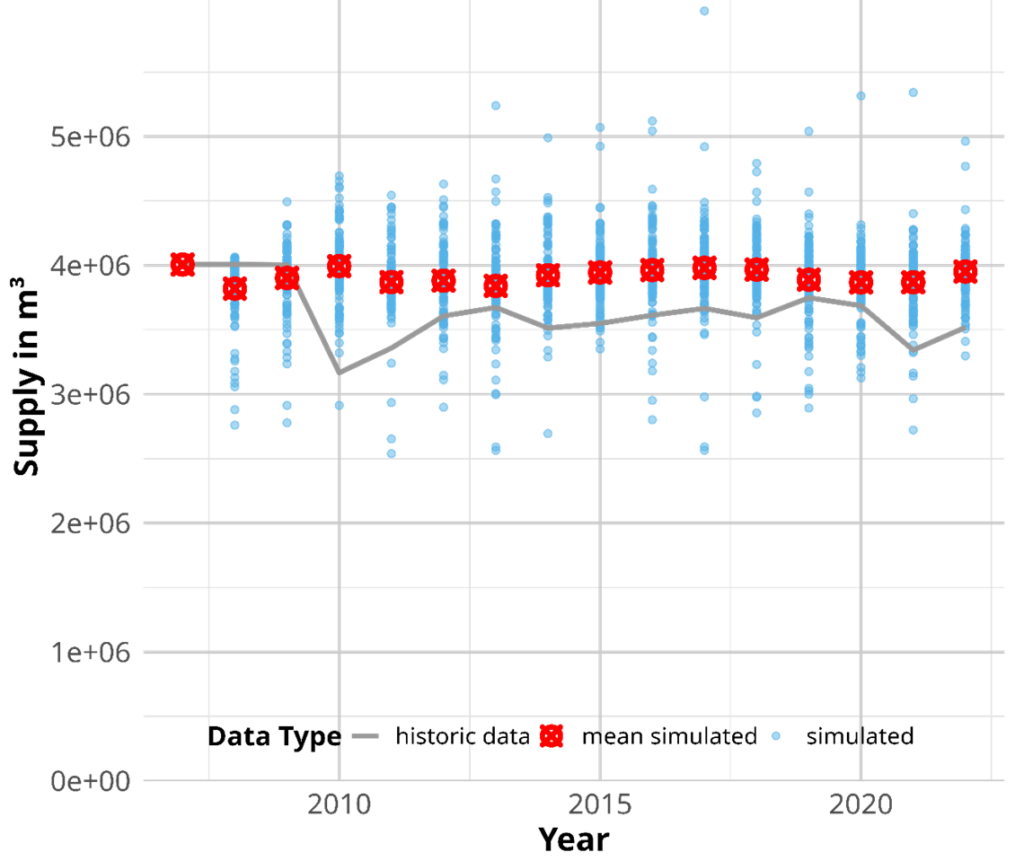
International forest-based supply chains face inherent risks and uncertainties stemming from diverse factors, including political and climate change, market fluctuations, and supply disruptions. Agent-based modeling (ABM) provides an approach to improve the understanding of the complex interactions between natural, social, and economic factors. ABM consists of autonomous agents and their environment, utilising a bottom-up modeling approach where complex system states emerge from the behaviors of individual components. We developed the design of an empirically based ABM focusing on international markets within forest-based supply chains, aiming to gain insights into factors influencing resource availability. The modeling framework incorporates five distinct agent species: foresters, sawmills, intermediaries, producers, and consumers. The modelling environment consists of a forest module and four market modules. In this round-based simulation, agents either act as suppliers or demanders negotiating based on their inventories and price expectations. Each stakeholder group is highly dependent on upstream and downstream markets. Other markets and macroeconomic developments are considered but not explicitly modeled, thus defining the model boundaries. While the model is implemented with data from multiple sources, abstract parameters were determined by calibration. Simulation results were validated with historical production data of the modelled nations. Integrating empirical data can enhance the realism and relevance of ABMs, but it necessitates a thorough understanding and analysis of the input data. The developed model serves as a platform to assess what-if scenarios, wherein agents follow defined sets of rules that can be modified, as for example adjusting demand, production capacities or preferences in suppliers. This allows to test effects of various policies and agent strategies. Furthermore, the model facilitates the examination of market disruptions resulting from e.g. environmental changes. Simulating the impact of these disruptions provides insights into the system’s vulnerability to changing conditions, crucial to foster sustainable development and avoiding unintended repercussions.